
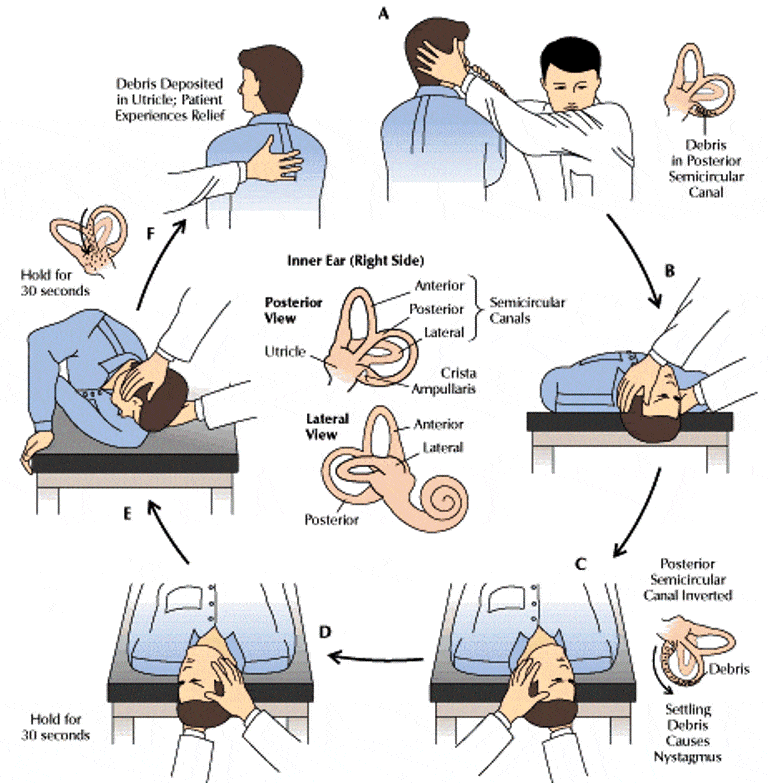
Box 1 provides an overview of specific treatments for the most common peripheral vestibular disorders. 2 Initial treatment varies, depending on the most likely vestibular disorder. Most cases of vertigo are caused by peripheral vestibular disorders such as vestibular neuronitis, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, vestibular migraine, and Ménière’s disease. 2 Since the symptoms of vertigo prevent many people from working, as well as resulting in an increase in the risk of falling and a high use of healthcare services, vertigo also represents a substantial economic cost. 2 Around 80% of these people affected by vertigo find that it severely impairs their daily functioning. Our results indicated that while promethazine cures peripheral vertigo more efficiently, ondansetron is more beneficial for the improvement of nausea and. 1 Each year around 1 in 20 people in the general population experiences vertigo. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. Currently patients are generally treated in general practice with betahistine (off-label use), while stronger evidence exists for the effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation. Patients with chronic vertigo who do not respond to disease-specific treatments should be offered vestibular rehabilitation instead of anti-vertigo drugsĬhronic vertigo is a challenging problem. Vestibular rehabilitation is a form of exercise therapy designed to optimise the process of vestibular compensation that is disrupted in patients with chronic vertigo Patients with vertigo should first be treated with any specific treatment for the underlying vestibular disease


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
